Economic overview of the fruit and vegetable sector : production, trade and consumption
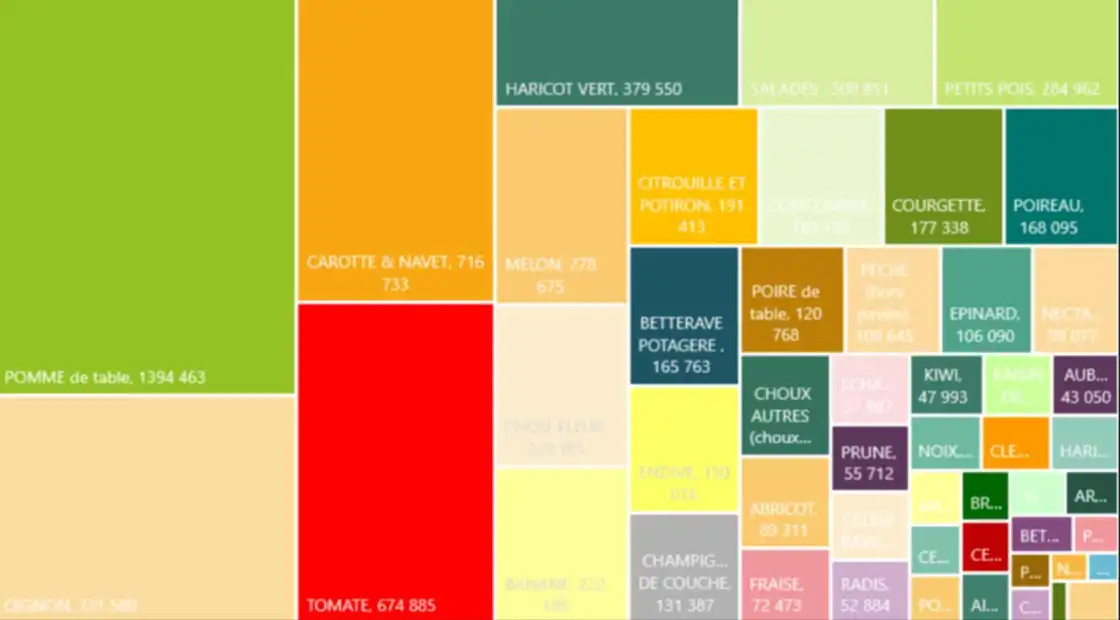
Overview of fruit and vegetable production in France
This talk, presented at SIVAL 2025 by CTIFL, highlighted the evolution of fruit and vegetable production in France. National fruit and vegetable production fell by 2% overall between 2010 and 2023. This trend is contrasted between vegetables, whose production increased by 2.8%, and fruit, whose production fell by 11%. Among the most widely produced species are table apples, onions, carrots and tomatoes.
In terms of geographical distribution, Occitanie is the leading fruit-producing region, with over 560,000 tonnes produced annually. France ranks fourth among European producers, behind Spain, Italy and Poland. In terms of processing, 25% of national production goes to the food industry for the manufacture of preserves, compotes and frozen foods.
Foreign trade in fruit and vegetables: a structural deficit
Foreign trade in fruit and vegetables is marked by a growing trade deficit, reaching -5.4 billion euros in 2023. This deficit is due to a rapid increase in imports, while exports are growing at a more moderate pace. The balance of trade in volume thus amounts to -3.3 million tonnes.
Imports come mainly from Spain, the leading supplier of fruit and vegetables, accounting for a third of imported volumes. Outside the European Union, Latin America and Africa supply France with exotic or out-of-season produce. On the export side, Spain is also the main customer, notably for apples, pears and bananas. Other preferred destinations are the United Kingdom and Germany. Spain still dominates vegetable imports, followed by Morocco, the Netherlands, Belgium and Italy.
Fruit and vegetable consumption trends
Fruit and vegetable consumption in France is influenced by several factors, including household purchasing power. Official recommendations call for a daily intake of 400 grams of fruit and vegetables, equivalent to five portions a day. However, only 32% of adults respect this recommendation, a proportion that drops to 10% among children.
Since 2021, consumption has fallen, due to the inflationary context which has led households to reduce their purchases of fresh produce. This trend is particularly noticeable in the organic market, whose market share has been declining since 2020. On the other hand, certain fruit and vegetable categories are enjoying dynamic growth, such as red berries, avocados and mangoes. Conversely, traditional products such as apples, oranges and bananas are stable.
Consumer profiles reveal a correlation between age and purchasing habits. The over-50s over-consume fresh fruit and vegetables, while young adults consume less than the average. One of the challenges for the sector is therefore to capture these younger generations and reverse the downward trend in fresh produce purchases.
Speakers
ANNE LAURE LEVET - Director of Prospective and Economic Studies - CTIFL